Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Defined
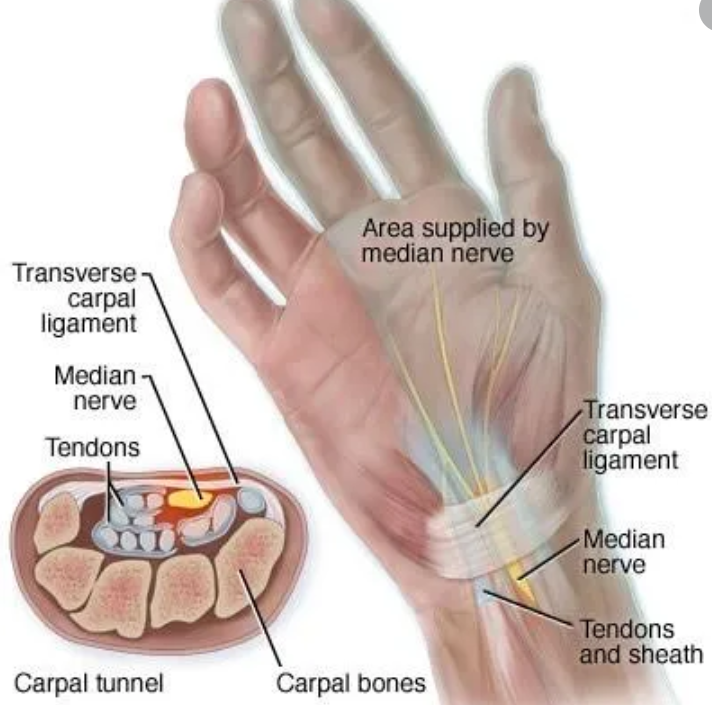
CTS is a condition where the median nerve in the arm is compressed or damaged, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. It occurs when the median nerve, one of the major nerves in the arm, is compressed as it travels through the carpal tunnel. This nerve can be compressed by the transcarpal ligament or the various flexor tendons that it resides next to in the wrist (see picture). CTS affects more than 12 million people nationwide and will affect ~10% of the population at some point in their lives.
What are the Risk Factors of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)?
CTS is more likely to occur in people with hypothyroidism, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, history of wrist trauma or pregnancy. All of these conditions predispose people to swelling of the tendons in the wrist and thus limit the area that the median nerve can reside in. When the median nerve’s space is compromised compression can occur and the patient can experience numbness, tingling and weakness in the skin and muscles that the nerve supplies.
How is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treated?
Initially, CTS can be treated with bracing, stretching, behavioral modification, and NSAIDs. It may also be treated with steroid or platelet injections. However, if symptoms persist it is typically recommended that patients undergo a surgical procedure to cut the ligament of the carpal tunnel and give the nerve more space.
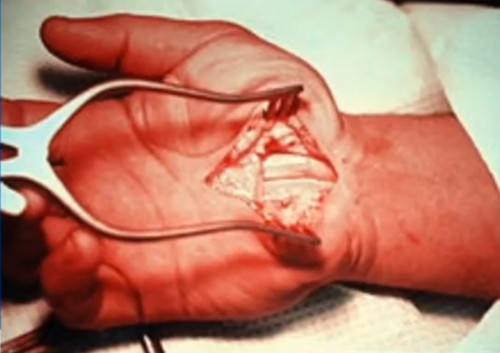
Traditional Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
CTS surgery is called carpal tunnel release (CTR), which relieves pressure on the median nerve by cutting the transverse carpal ligament. Traditional CTR procedures can remedy the condition but may result in large and sometimes painful scars, ongoing palmar pain, and a longer road to recovery.
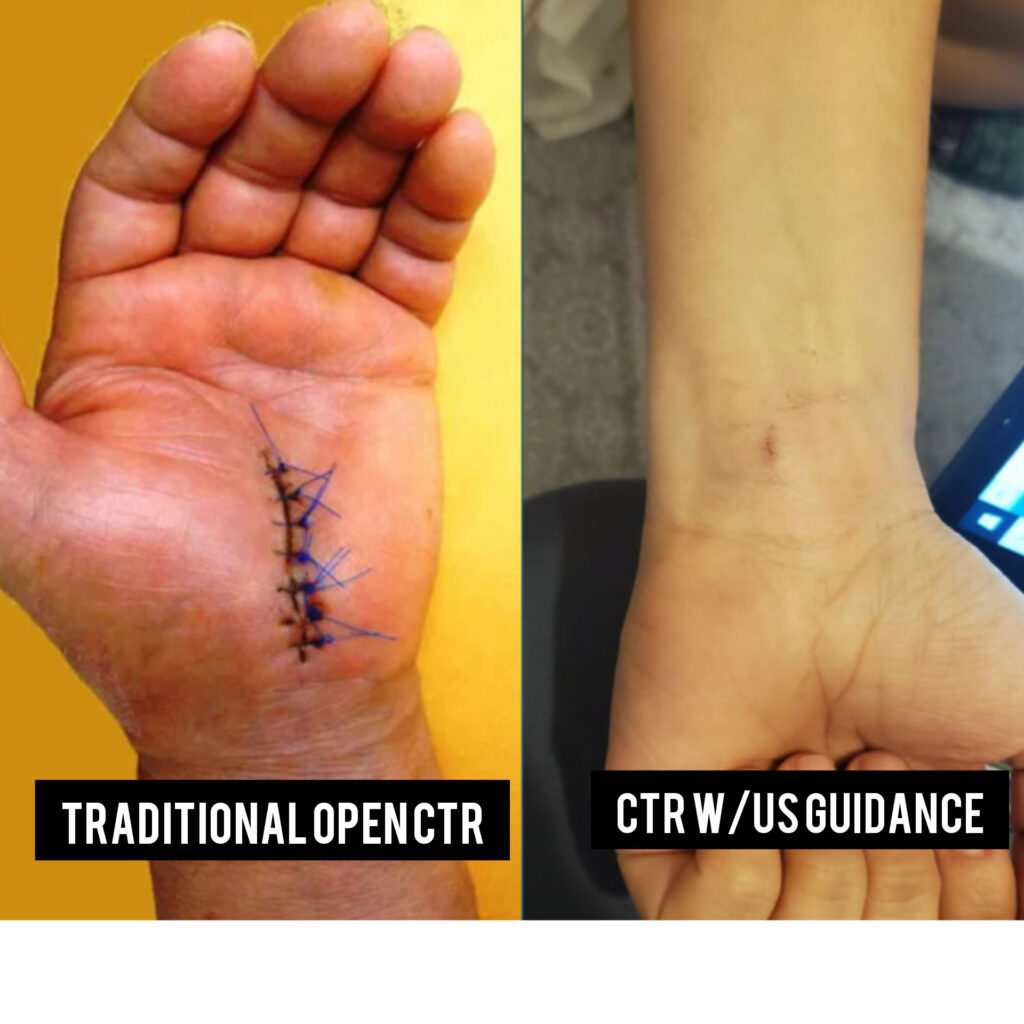
A Proven Minimally Invasive Approach to Treat Carpal Tunnel Syndrome for Faster Recovery
Now there’s a proven way to get rapid relief from carpal tunnel pain and return quickly to normal activities.
CTR with ultrasound guidance
This procedure involves a safe, and effective instrument that allows the doctor to perform carpal tunnel release in a matter of minutes. When combined with ultrasound visualization, the procedure requires only a very small (3-4 mm) wrist incision.
Significant Benefits of the procedure
- Performed in a procedure room or office setting
- Can be performed using local anesthesia
- Small wrist incision is typically closed without sutures
- Reduces or eliminates the need for opioids
- Postoperative therapy is typically not required—saving you time and money
- Immediate motion in the hand for rapid recovery
- Return to normal activity in a few days, not months
After the procedure, you’ll be able to resume activities as tolerated—most patients can return to work and the activities they love within 3-6 days.
If you or someone you know is interested in this innovative procedure, please contact us today.
References:
- Nakamichi K, Tachibana S, Yamamoto S, et al. Percutaneous carpal tunnel release compared with mini-open release using ultrasonographic guidance for both techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 2010 Mar;35(3):437-445.
- Rojo-Manaute JM, Capa-Grasa A, Chana-Rodriguez F, et al. Ultra-minimally invasive sonographically guided carpal tunnel release: a randomized clinical trial. J Ultrasound Med. 2016 Jun;35(6):1149-1157.



