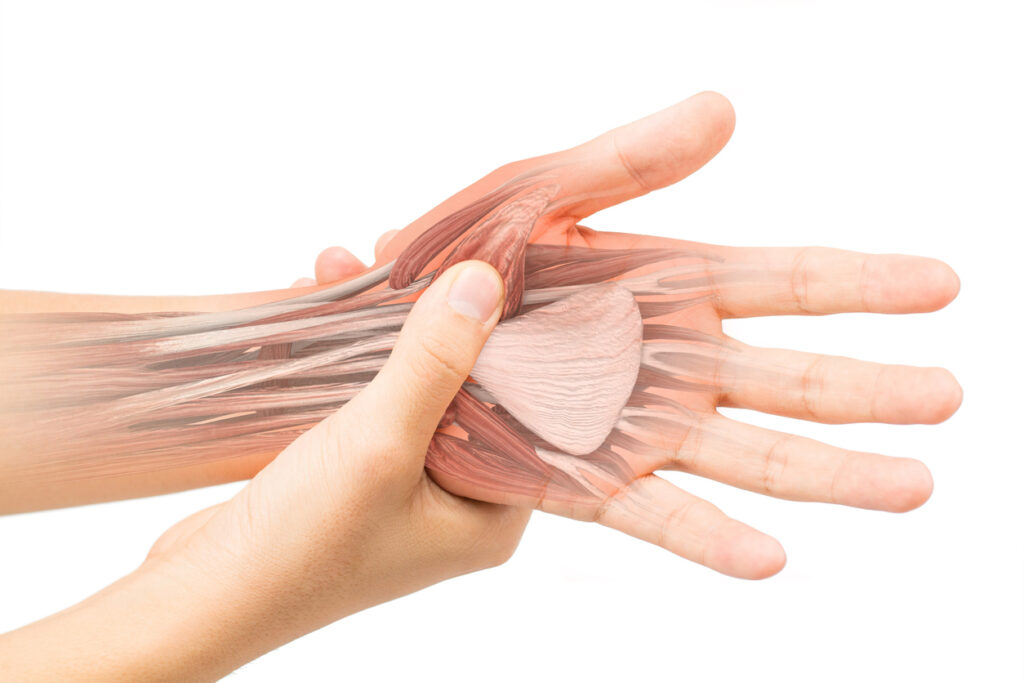
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) affects more than 12 million people nationwide and will affect ~10% of the population at some point in their lives. Why is this such a prevalent condition and what is the anatomy behind CTS?
The Carpal Tunnel is ostensibly a choke point in the wrist. The floor of the carpal tunnel is created by the carpal (wrist) bones and the roof is formed by the transverse carpal ligament. Meanwhile, the median nerve and 9 other tendons pass through the carpal tunnel between the carpal bones and the transverse carpal ligament. These other tendons are the flexor digitorum superficialis tendons(4), the flexor digitorum profundus(4) and the palmaris longus tendon(1). See the picture below.
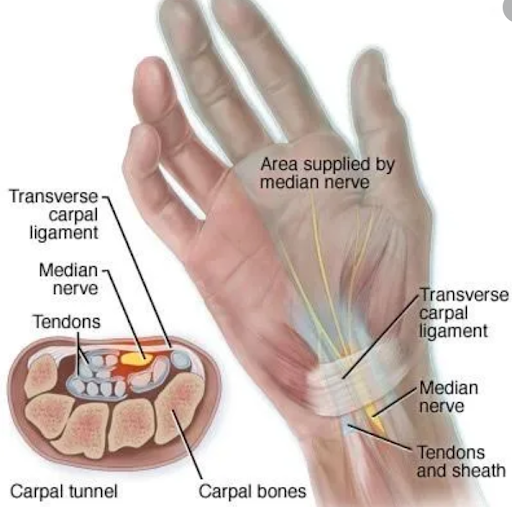
How Does Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Occur?
CTS occurs when the median nerve is compressed or damaged at the carpal tunnel. Typically, this is from thickening of the transverse carpal ligament, thickening of the flexor tendons and the resulting lack of room for the median nerve. When the median nerve is injured, this can lead to pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. Often these symptoms are worse with repetitive motions or with sleep.
There are some anatomical variations that can increase the risk for CTS. One of the most common is called a bifid median nerve, meaning that the median nerve is divided into 2 distinct bundles at the carpal tunnel. This appears to increase the risk for CTS as a bifid median nerve is larger and more likely to become compressed. See the ultrasound image below.
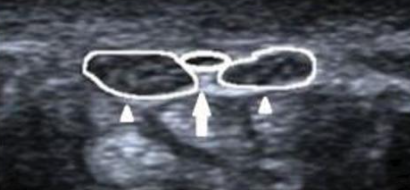
What Are The Risk Factors Of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)?
CTS is also more likely to occur in people with diabetes, hypothyroidism, rheumatoid arthritis, a history of wrist trauma, or pregnancy. All of these conditions predispose people to swelling of the tendons in the wrist and thus limit the area that the median nerve can reside in.



